In today’s digital era, data has become one of the most valuable assets for individuals and organizations alike. As the volume of data continues to grow exponentially, so do the threats targeting it. Cyberattacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access have become commonplace, making the protection of personal and sensitive information a top priority. This is where the intersection of cybersecurity and data privacy comes into sharp focus. While often discussed as separate disciplines, cybersecurity and data privacy are deeply intertwined, with robust cybersecurity practices forming the backbone of effective data privacy.
For individuals just starting their journey into this field, cyber security training for beginners is essential. It provides the foundational knowledge needed to understand these critical concepts, equipping them with the tools to protect data and maintain privacy in today’s digital landscape.

Understanding the Relationship Between Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
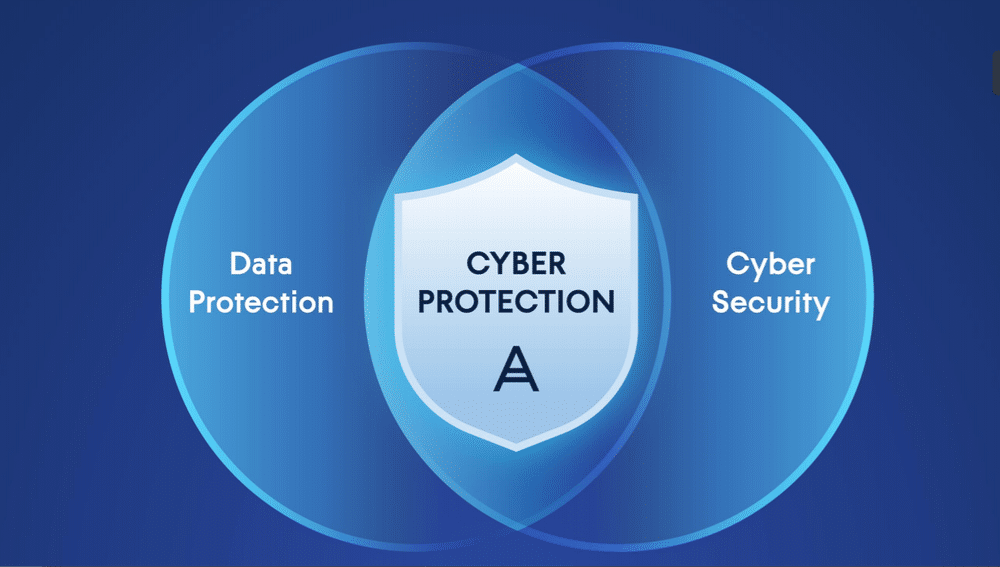
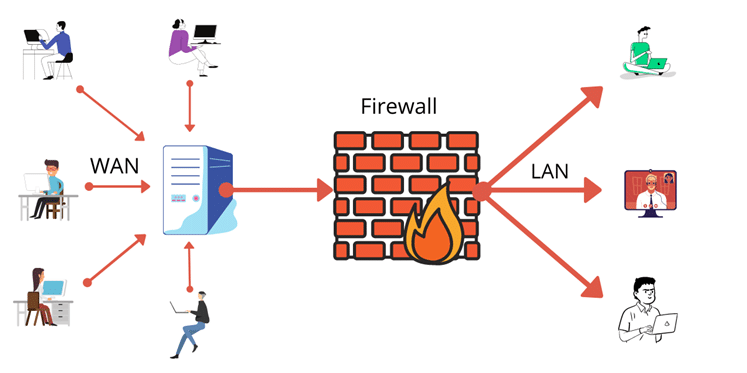
At their core, both cybersecurity and data privacy aim to protect data, but they approach the task from different angles. Cybersecurity is primarily concerned with safeguarding data from external and internal threats, such as hackers, malware, and unauthorized access. It involves implementing technical measures like firewalls, encryption, intrusion detection systems, and secure access controls to prevent breaches and protect the integrity of data.
Data privacy, on the other hand, focuses on ensuring that data is collected, processed, and shared in a way that respects individuals’ rights and complies with legal requirements. It addresses questions of who has access to data, how data is used, and how individuals can control their personal information. While cybersecurity protects data from threats, data privacy ensures that data is handled responsibly and transparently.
Despite these different focuses, cybersecurity and data privacy are mutually reinforcing. Without strong cybersecurity measures, even the best privacy policies and practices can be rendered ineffective. Conversely, cybersecurity efforts that don’t consider privacy can lead to overreach, where too much data is collected or shared without adequate protections, ultimately undermining trust.
How Cybersecurity Practices Enhance Data Privacy
- Data Encryption
- One of the most fundamental cybersecurity practices, encryption, plays a crucial role in data privacy. By encrypting data both in transit and at rest, organizations ensure that even if data is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized individuals, it remains unreadable and secure. Encryption is a cornerstone of privacy, as it protects sensitive information from exposure and misuse.
- Access Controls and Authentication
- Cybersecurity strategies often include robust access controls and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive data. These measures help to enforce the principle of least privilege, where users are granted only the access they need to perform their duties. By controlling who can access data, organizations can prevent unauthorized data sharing and breaches, thereby upholding privacy.
- Intrusion Detection and Response
- Cybersecurity practices such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) and incident response plans are essential for quickly identifying and mitigating breaches. When a breach occurs, the speed and effectiveness of the response are critical to minimizing the impact on data privacy. A well-coordinated incident response not only contains the threat but also ensures that affected individuals and regulators are promptly notified, preserving trust and compliance with privacy laws.
- Data Minimization
- A key principle in both cybersecurity and data privacy is data minimization—collecting only the data that is necessary for a specific purpose and retaining it only as long as needed. Cybersecurity practices that focus on data minimization reduce the amount of data at risk in the event of a breach, thereby enhancing privacy protections.
- Regular Audits and Compliance Checks
- Ongoing cybersecurity audits and compliance checks are vital for maintaining both security and privacy. These audits assess the effectiveness of security controls, identify potential vulnerabilities, and ensure that privacy practices are in line with regulatory requirements. Regular audits help organizations stay ahead of evolving threats and changing privacy laws, ensuring that both security and privacy measures are up-to-date.
- Employee Training and Awareness
- Human error is a leading cause of data breaches and privacy violations. Cybersecurity training programs that educate employees about the importance of data protection, the latest threats, and best practices for secure behavior are essential for maintaining robust data privacy. When employees understand the role they play in safeguarding data, they are more likely to follow protocols that protect both security and privacy.
The Benefits of Integrating Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
When cybersecurity and data privacy are integrated, organizations benefit from a more holistic approach to data protection. This integration ensures that data is not only secure from external threats but also handled in a way that respects individuals’ privacy rights. By aligning cybersecurity practices with privacy objectives, organizations can:
- Enhance Trust: Demonstrating a commitment to both security and privacy builds trust with customers, clients, and partners. In an age where data breaches make headlines, trust is a critical asset.
- Ensure Compliance: Many data protection regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, require both strong security measures and privacy practices. Integrating these disciplines helps organizations meet compliance requirements more effectively.
- Reduce Risk: A comprehensive approach to data protection reduces the risk of breaches and privacy violations, minimizing potential legal and financial consequences.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the clear benefits, integrating cybersecurity and data privacy can be challenging. It requires a coordinated effort across different teams and departments, as well as ongoing investment in technology and training. Additionally, organizations must balance the need for strong security with respect for privacy, avoiding practices that could lead to excessive data collection or surveillance.
Conclusion: A Unified Approach to Data Protection
The intersection of cybersecurity and data privacy is where true data protection happens. By treating these disciplines as two sides of the same coin, organizations can build a more resilient defense against the myriad threats facing their data. In an era where data breaches and privacy concerns are at the forefront of public consciousness, a unified approach to cybersecurity and data privacy is not just a best practice—it’s a necessity.
For those looking to equip themselves with the skills needed to protect data effectively, enrolling in a cyber security course in Chennai is an excellent step toward mastering these critical areas. This type of training provides practical knowledge and insights to help individuals and organizations strengthen their data protection strategies.